Configuring And Using Segments
Well-known ways to segment your audience
Demographics
Breakdown by any combination: age, gender, income, education, ethnicity, marital status, education, household (or business), size, length of residence, type of residence, or even profession/occupation.
An example is Firefox which sells ‘coolest things’, aimed at the younger male audience. Moshi Monsters, however, is targeted at parents with a fun, safe, and educational space for younger audiences.
Firmographics
This refers to ‘personality and emotions’ based on behavior, linked to purchase choices, including attitudes, lifestyle, hobbies, risk aversion, personality, and leadership traits. magazines read and TV. While demographics explain ‘who’ your buyer is, psychographics informs you of ‘why’ your customer buys.
There are a few different ways you can gather data to help form psychographic profiles for your typical customers.
- Interviews: Talk to a few people who are broadly representative of your target audience. In-depth interviews let you gather useful qualitative data to understand what makes your customers tick. The problem is they can be expensive and difficult to conduct, and the small sample size means they may not always be representative of the people you are trying to target.
- Surveys: Surveys let you reach more people than interviews, but it can be harder to get insightful answers.
- Customer data: You may have data on what your customers tend to purchase from you, such as data coming from loyalty cards if an FMCG brand or from online purchase history if you are an e-commerce business. You can use this data to generate insights into what kind of products your customers are interested in and what is likely to make the purchase. For example, does discounting vastly increase their propensity to purchase? In which case they might be quite spontaneous.
Lifestyle
This refers to Hobbies, recreational pursuits, entertainment, vacations, and other non-work time pursuits.
Companies such as on and offline magazines will target those with specific hobbies i.e. FourFourTwo for football fans.
Some hobbies are large and well established, and thus relatively easy to target, such as the football fan example. However, some businesses have found great success targeting very small niches very effectively. A great example is an explosion in ‘prepping’ related businesses, which has gone from a little heard-of fringe activity to a billion-dollar industry in recent years. Apparently now 3.7 million Americans think of themselves as preppers or survivalists. A great way to start researching and targeting these kinds of niches is Reddit, where people create subReddits to share information about a given interest or hobby.
Belief and values
Refer to Religious, political, nationalistic, and cultural beliefs and values.
The Islamic Bank of Britain offers Sharia-compliant banking which meets specific religious requirements.
A strange but interesting example of religious demographics influencing marketing that you might not have guessed is that Mormons are really into ‘multi-level marketing. They’re far more likely to be engaged in the practice than any other US group. Going the extra mile with demographic research can lead to discovering new marketing opportunities and thinking outside the box. For example, did you know the average age of a Cadillac driver is 47.1 years old? But you don’t tend to see them in the car ads. An opportunity waiting to be seized!
Life stages
Life stages are the Chronological benchmarking of people’s lives at different stages.
An example is the Saga holidays which are only available for people aged 50+. They claim a large enough segment to focus on this life stage.
Geography
Drill down by Country, region, area, metropolitan or rural location, population density, or even climate.
An example is Neiman Marcus, the upmarket department store chain in the USA that now delivers to the UK.
Behavior
Refers to the nature of the purchase, brand loyalty, usage level, benefits sought, distribution channels used, and reaction to marketing factors.
In a B2B environment, the benefits sought are often about ‘how soon can it be delivered?’ which includes the ‘last-minute’ segment – the planning in the advance segment.
An example is Parcelmonkey.co.uk which offers same-day, next-day, and international parcel deliveries.
Benefit
The benefit is the use and satisfaction gained by the consumer.
Smythson Stationery offers similar products to other stationery companies, but their clients want the benefit of their signature packaging: tissue-lined Blue Nile boxes tied with a navy ribbon!
Using Segmentation
Easily segment your leads into lists automatically create detailed segments of leads based on specific properties and actions, or manually add leads to a segment to create lists for more personalized marketing. Monitor the growth and activity of your lists with Jacktrade’s list analytics.
Segmentation means dividing the marketplace into parts, or segments, which are definable, accessible, actionable, profitable, and have growth potential. In other words, a company would find it impossible to target the entire market, because of time, cost, and effort restrictions. It needs to have a ‘definable’ segment – a mass of people who can be identified and targeted with reasonable effort, cost and time.
Setting Up Segmentations
Segments can be set up easily in Jacktrade with the perfectly designed user-friendly interface. All you need to do is name the segment correctly and set up the correct rule sets to segment the customers. The rules setup is based on the functions (Profiling, Quotes, Jobs, Opportunities, and Products) and corresponding exposed keys that are exposed from the system to retrieve the value to apply and construct arguments that build segmentation.
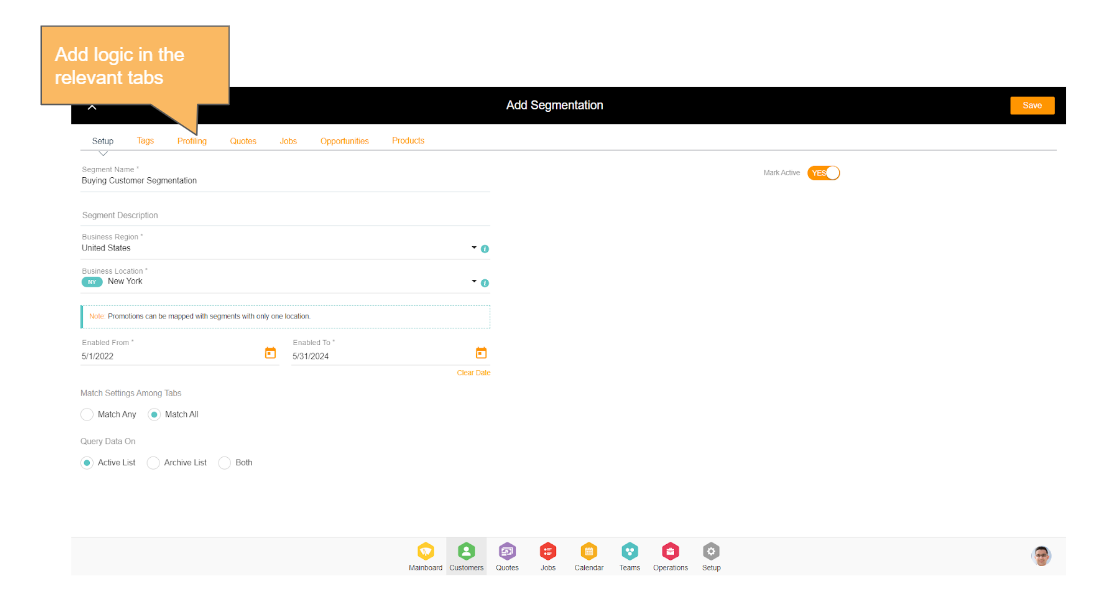
Navigation Reference: Segmentation → Add Segmentation
Implementing a Better Market Segmentation
- Objective Setting
- Set segmentation objectives and goals
- Identify segmentation variables and develop a hypothesis
- Identify Customer Segments
- Research design
- Data collection
- Analyze data and identify segments
- Validate all results
- Develop Segmentation Strategy
- Select target segment
- Identify segmentation implications & recommendations
- Execute Go-To-Market Plan (launch plan)
- Identify key stakeholders
- Develop communications & operational launch plan
- Execute and monitor
Business Location Mapping
Segmentation’s primary focus is to segregate customers into various needs of the business. Each segment maps to multiple locations within a region to match the customers that are globally available. It is possible that a single segment can map to customers that are outside the region because customers do not belong to a specific region – they are global in Jacktrade.
Setting Up Exposed Keys
All keys are subjected to the following categories. These categories derive a range or specific values as needed.
- Data Value – the value of the data like “Male” in gender for demographics, or tag name like “sales funnel”.
- Date – from and to a range of the date, for example, Customer purchase between September 15th to October 15th
- Status – the status value of a function, for example, Quote status, Visit status, Opportunity status
- Type – service type, for example, Quote service type, visit type, product type, etc.
- Age – pre-calculated pre-age of a particular function like Age of a Quote or Job, or Support case.
- Amount – Amount associated with the key.
- Year – from and to a range of the year for example Product bought between year X and Y.
- Count – pre-calculated values like number of Jobs, number of visits, etc.
- Business Location – Location attached to the calling function.
- Target Resources – Resources attached to the calling function like Opportunity Case assigned to Sales Associate, or Resources assigned to Recurring Services. This is not used in segmentation.
- Target Customer – Customer attached to the calling function like a customer assigned to Jobs. This is not used in segmentation.'
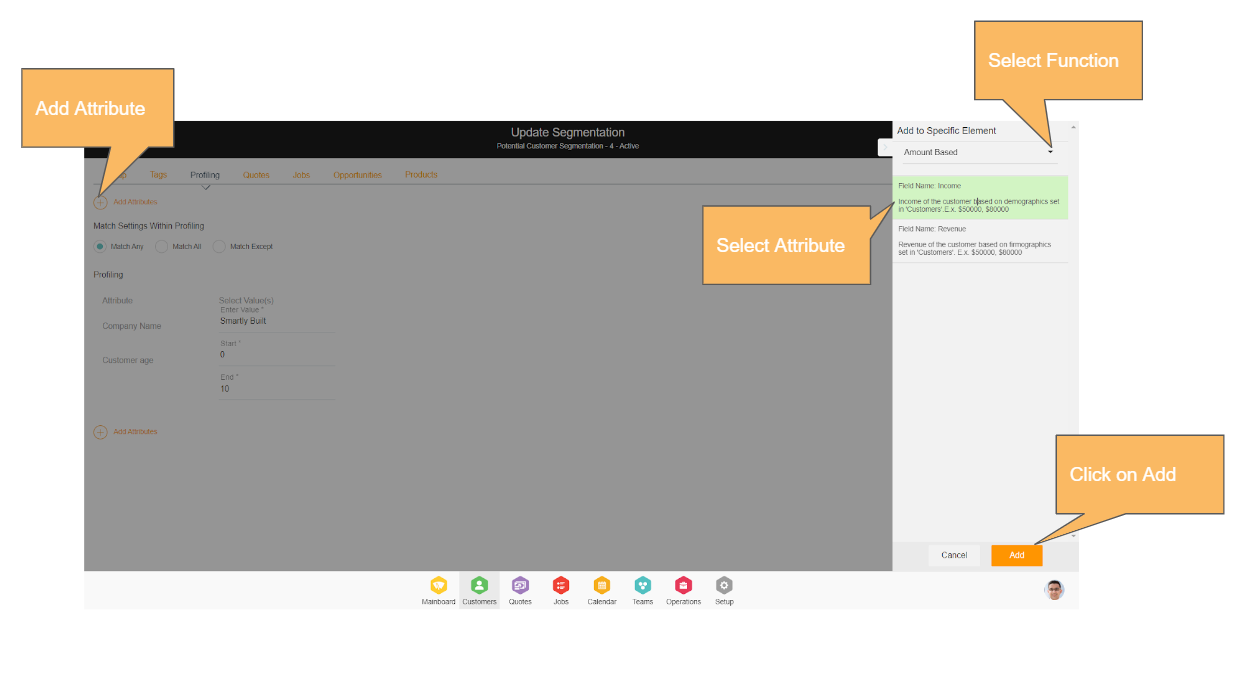
Navigation Reference: Segmentation → Add Segmentation
Selecting the Correct Input Type
Conditions like date range, amount range, and character type are identified using data types. Based on the data types, the UI will represent the correct input. Data field input fields show data directly belonging to the business like ‘service type’, and other fields show a range between certain values. Almost all fields have multiple select options.
Constructing Argument
Once the segment rule is saved, the back end constructs a proper argument and stores the argument. Arguments are used every time segmentation is queried for the list.
Rules Used as part of the arguments
- Master Matcher
- Match all
- Match any
- Match Except for
- Query On which data
- Active List
- Archive List
- Both Active and Archive
- Date-based Rules
- Date is
- Date is between
- Age-based Rules
- Age is
- Age is between
- Numeric Comparisons
- Is equal to
- Is Between
Identifying Changes in Rule
Rules are only reconstructed upon a change in customer segmentation rules. The application identifies if the rules have changed or if the user just pressed ‘save’ without any changes.
Reconstructing Rules upon Change
Upon rules change, segmentation checks for any other modules that are utilizing this particular segmentation like Promotions and Nurturing. Users can change segmentation rules anytime, and this change checks two things:
- If there are NO dependencies (NO campaigns, notifications, and promotions are referencing this segmentation), then the segmentation simply changes, and the list is reconstructed.
- If there are dependencies (campaigns, notifications, and promotions referencing this segmentation), it provides the user if there is any interference with the mapped functions.
Enabling a Segment
When enabling a disabled segment, the system will find out what corresponding functions are mapped with it like promotions, Guided Action lists, and Nurturing templates. The system will just show the user the count of corresponding functions but will NOT ENABLE them when enabling the segment. The user will have to go to each function and ENABLE it separately.
Disabling Segmentation
Segmentation can be disabled if the user is provided the same acknowledgment informing of the interference. Other dependent functions using this segmentation will perform the following:
- Campaigns – The corresponding campaigns will be“disabled”.
- Promotion – The corresponding promotions will be“disabled”.
- Notifications - The corresponding notifications will be“disabled”.
- Smart Actions - The corresponding actions will be “disabled”.
Disabling an active segment will affect the following functionalities in the application – Promotions, Guided Action Plans, Nurturing, notifications, and Lead Generation.
User Experience When Disabling Segmentation
Every time a user disables a segment, an acknowledgment pop-up with all the information of the dependencies like the number of promotions getting affected, several GALs (Guided Action List) getting affected, etc will be shown to the user. On confirmation only, that the user wants to proceed with disabling, the segment will be disabled.
It will work the same way for archiving a segment.
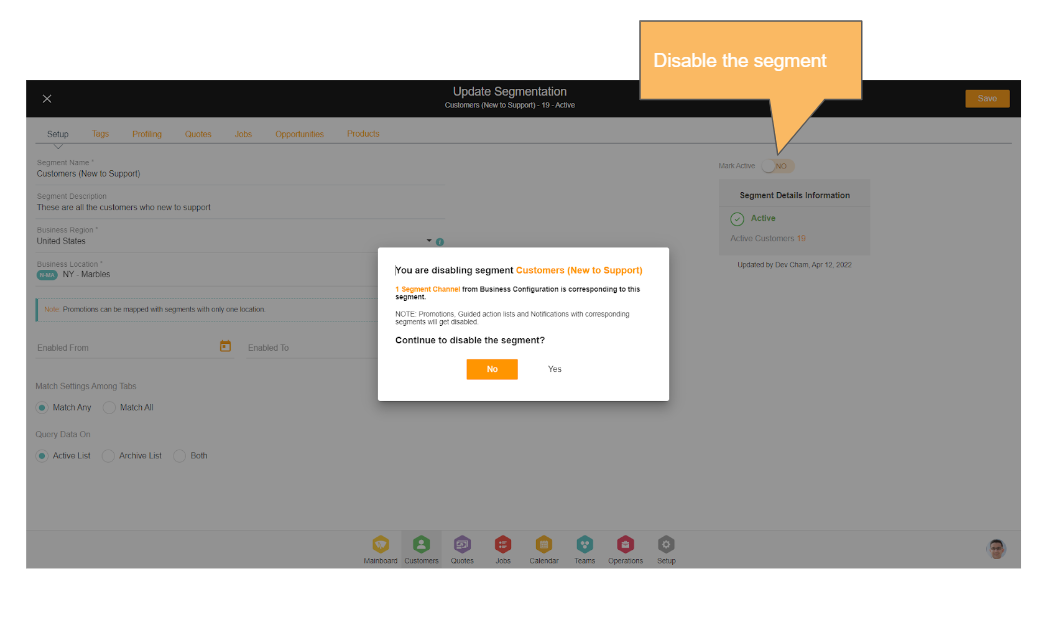
Disabling Segmentation – Promotions
Disabling a segment that is mapped with the promotions will disable the promotions corresponding to promotions. Once the promotions are disabled –
- Does not allow for any new promotions to be viewed, applied, or utilized.
- Existing promotions are marked with the status “Unavailable” in Quote or Job after Quote to Job checks that this promotion is archived.
- If the previous promotion is no longer valid, then the Quote status changes to “Modified” if submitted already.
- Invalid promotions that are applied to the Quote or Job will have to be removed before making payments or submitting a quote.
Disabling Segmentation – Guided Action Plans
Disabling a segment associated with a Guided Action list will disable the corresponding rules in the Guided Action list as well. Once the rules in GAL are disabled, the creation of action items based on the rule set defined in that particular GAL will be stopped from that point onwards.
Disabling Segmentation – Nurturing
Disabling a segment associated with a campaign list will disable the corresponding campaign list as well. Once the campaigns are disabled, the emails going out for those campaigns will be stopped from that point onwards.
Viewing Customers as part of the Segment
Segmentation is utilized either by making dynamic calls or by grabbing the list and storing it locally for usage. For example, promotions will query on the spot in real-time, and nurturing will require downloading the list locally.
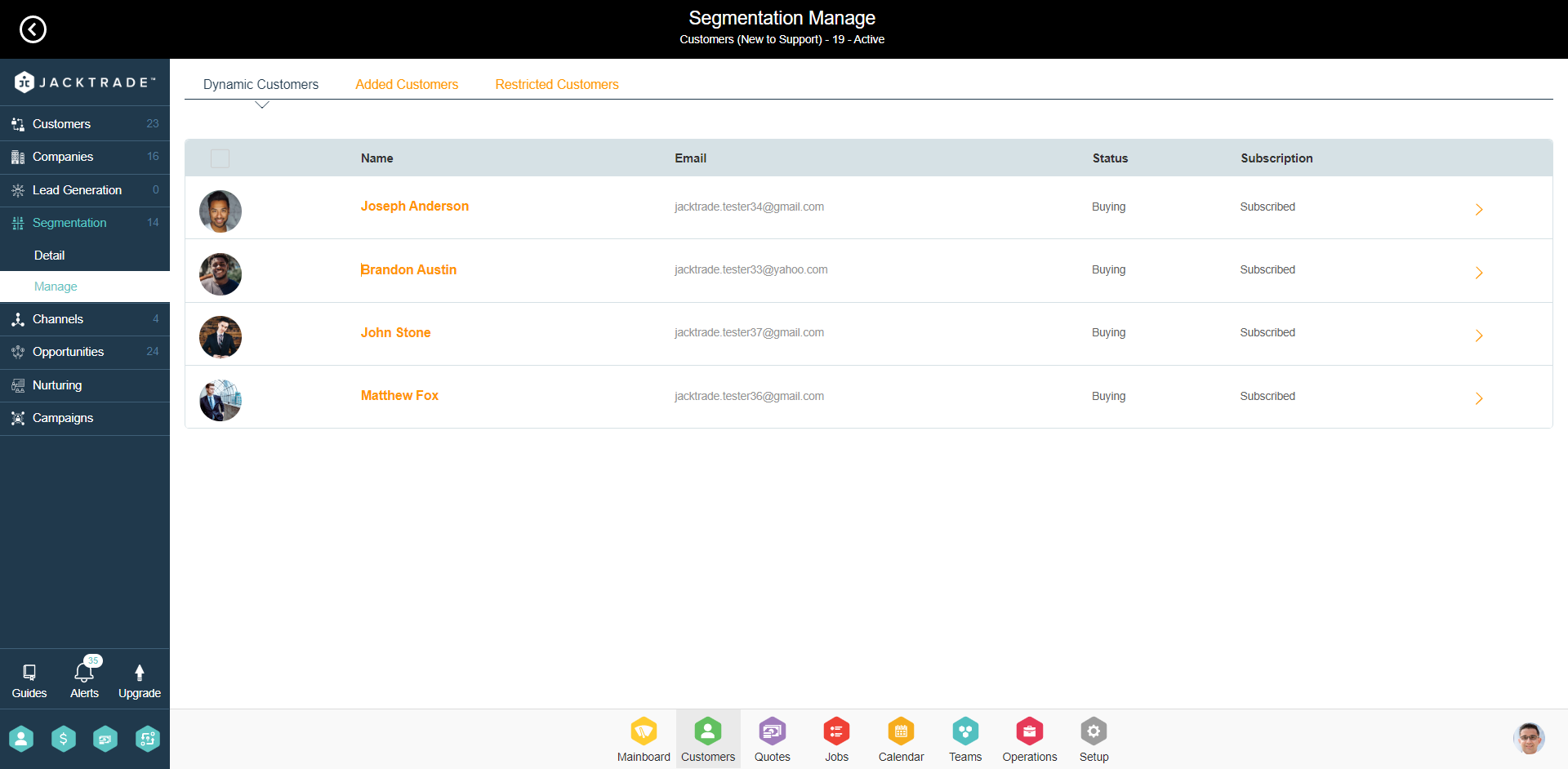
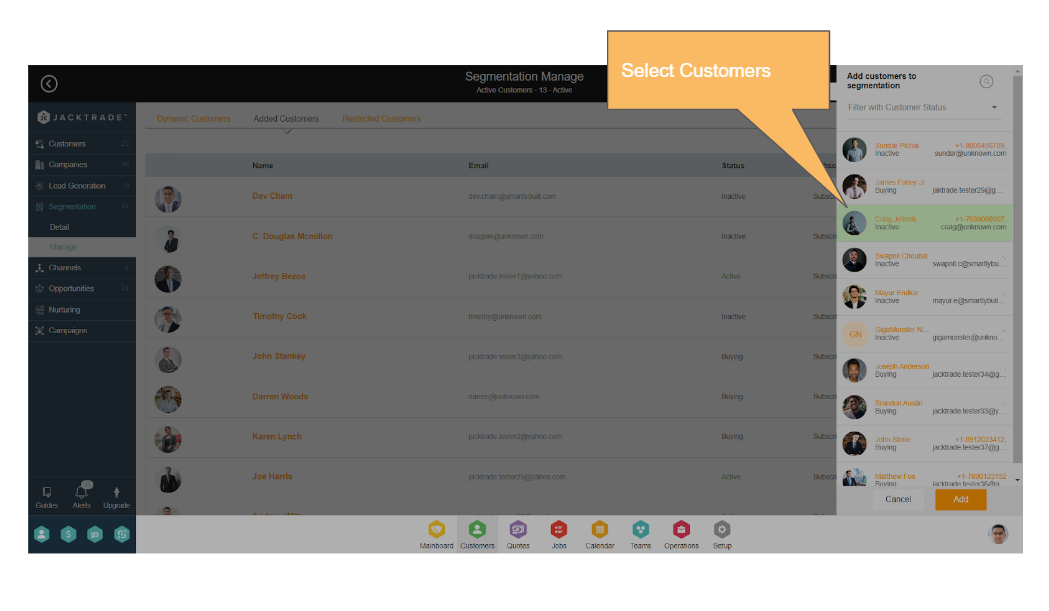
Adding Customers Manually
Users can add customers manually to the segmentation. This list only shows users that are not already assigned to the dynamic customer lists, manual customer lists, and restriction customer lists. Users can filter through customer status to narrow their search, and insert multiple customers at a time.
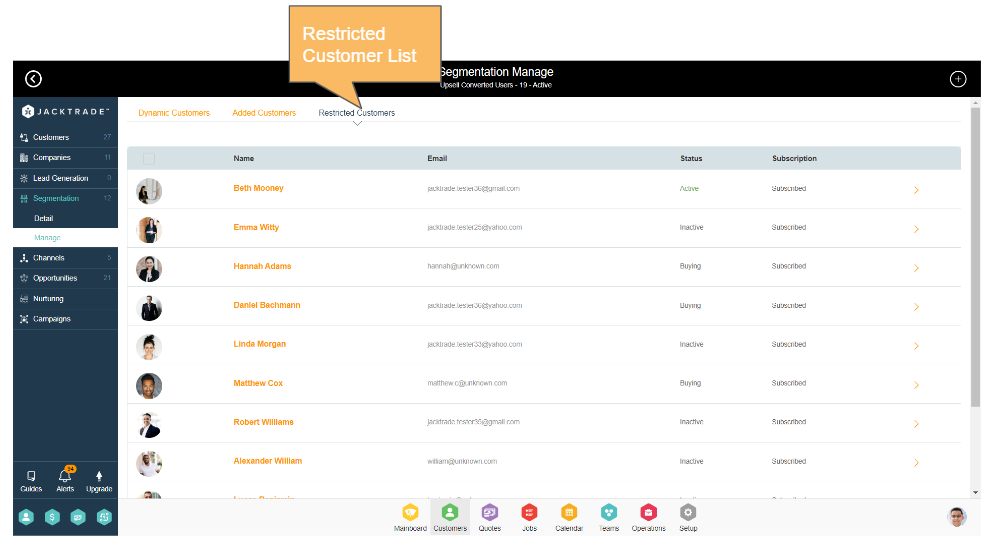
Restricting Customers from the Segment
Users can be restricted in the segment – this includes restricting customers that are not part of any of the three lists within the segmentation. Once restricted, any changes in constructing a customer list will consult this list and not add the restricted user to either dynamic or add a list.
Removing Duplicates
In segmentation, there could be a possibility that duplicate subscribers are found within the same segmented list. The argument construction finds only the subscriber/customer once.
Removing Common Email
There is a common email called “@unknown.com” that is rejected by the system if it's identified as part of the customer segment.
Showing Segments as part of the Customer Profile
Segments that the user belongs to is also shown as part of the customer profile. This gives users a quick view if a particular customer is a part of which segment instead of digging in each segment to identify where the customer is residing. The view shows a simple set of segments the customer is currently active. The table includes the following information:
- Segment Name – Name of the segment.
- Business Location – The business location segment is assigned to
- Active / Inactive – If the segment is active or inactive.
- Subscriber Since – Date when the customer has first subscribed to the segment.
- Updated By – User by which the segment was updated last.
Users can visit this segment directly from this table. There is no sorting, pagination, searching or filtering required.

